United Group Captive Insurance: A Deep Dive into Risk Management and Cost Savings
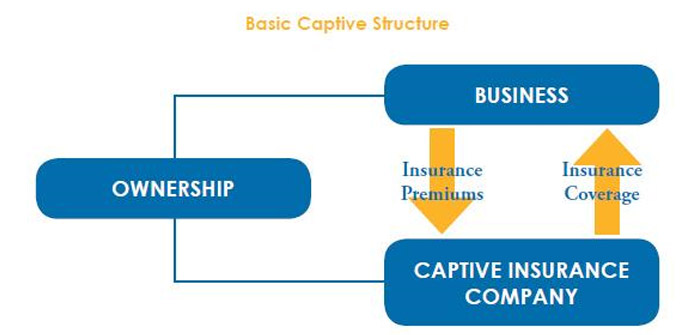
The complex world of risk management is constantly evolving, demanding innovative solutions for businesses seeking financial stability. Enter the United Group Captive Insurance model, a sophisticated approach that offers a compelling alternative to traditional insurance structures. This model allows a group of companies to pool their risks, creating a captive insurer owned and controlled by its members. This shared ownership fosters transparency and allows for greater control over risk assessment, claims management, and ultimately, cost savings. This in-depth analysis explores the intricacies of United Group Captive Insurance, examining its operational structure, regulatory landscape, and potential benefits. We’ll delve into risk management strategies tailored to this unique model, compare it to traditional insurance, and showcase successful implementations, highlighting key takeaways and future challenges. Defining United Group Captive Insurance United Group Captive Insurance represents a specialized form of insurance arrangement where a parent company, in this case, United Group, establishes its own insurance company to self-insure its risks. This differs significantly from traditional commercial insurance models, offering greater control and potential cost savings but also requiring substantial financial resources and expertise.This structure allows United Group to manage its risk profile more strategically, potentially reducing reliance on external insurers and improving transparency in its risk management processes. The key differentiator lies in the ownership and control; unlike traditional insurance where a third party underwrites and manages risk, a captive insurer is wholly owned and operated by the parent company. This inherent control provides a unique level of flexibility in risk assessment and management. Operational Structure and Governance United Group Captive Insurance operates under a defined governance structure, typically overseen by a board of directors responsible for strategic decision-making and compliance. This board comprises individuals with significant experience in insurance, risk management, and finance. Day-to-day operations are managed by a team of experienced insurance professionals responsible for underwriting, claims management, and regulatory compliance. The specific operational details and governance structure would be dictated by the jurisdiction in which the captive is domiciled and its internal policies. Robust internal controls and risk management frameworks are essential for the effective and compliant operation of such an entity. Regular audits and compliance reviews are conducted to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and internal standards. Transparency and accountability are paramount to maintaining the integrity and financial stability of the captive insurance operation. Benefits of a United Group Captive Insurance Structure A United Group Captive Insurance structure offers a compelling alternative to traditional insurance arrangements, providing significant advantages in risk management, cost savings, and enhanced financial stability for participating companies. This structure leverages the collective risk pooling of multiple entities to achieve economies of scale and greater control over insurance costs and claims management.The primary benefit lies in the enhanced risk management capabilities it provides. By pooling risks, the group mitigates the impact of individual losses, reducing the overall volatility of insurance costs. This proactive approach allows for more precise risk assessment and tailored coverage, addressing specific needs of the participating companies more effectively than standard, off-the-shelf policies. Cost Savings Through Risk Pooling and Premium Negotiation A key advantage of a United Group Captive is the potential for substantial cost savings. The pooling of risks allows for better premium negotiation with reinsurers, leading to lower overall insurance costs. Furthermore, the elimination of commissions and other intermediary fees common in traditional insurance models significantly reduces expenses. For example, a group of five similarly sized construction companies might see a 15-20% reduction in their combined insurance premiums compared to purchasing individual policies. This cost savings can be reinvested into the businesses, boosting profitability and growth. Enhanced Financial Stability Through Predictable Insurance Costs The predictability of insurance costs is a significant contributor to the enhanced financial stability of participating companies. Unlike traditional insurance, where premiums can fluctuate significantly year to year based on market conditions and individual claims experience, a United Group Captive provides greater stability. This predictable cost structure facilitates better financial planning and budgeting, reducing the risk of unexpected financial shocks. The shared risk also ensures that the financial burden of large claims is distributed across the group, preventing any single company from experiencing crippling losses. This stability is particularly valuable in volatile economic climates or industries prone to significant risk events. Improved Risk Management Practices and Loss Control The shared ownership and governance structure of a United Group Captive incentivizes participating companies to actively improve their risk management practices. Through shared knowledge and experience, best practices are readily exchanged, leading to enhanced loss control measures across the group. This collaborative approach fosters a culture of safety and risk mitigation, ultimately reducing the frequency and severity of claims, further enhancing cost savings and financial stability. For instance, a group of manufacturing companies might share safety protocols and training programs, leading to a demonstrable reduction in workplace accidents and associated insurance claims. Risk Assessment and Management within the United Group Captive Effective risk assessment and management are paramount for the success of any captive insurance program, particularly a United Group Captive. A robust framework ensures the captive remains financially sound and effectively protects the participating entities from unforeseen losses. This framework should be proactive, regularly reviewed, and adaptable to changing circumstances. Risk Identification and Categorization A comprehensive risk identification process is crucial. This involves systematically examining all potential risks faced by the member companies within the United Group. The process should be collaborative, involving risk managers from each member company and the captive’s management team. A structured approach, using techniques such as brainstorming sessions, checklists, and risk surveys, helps ensure a thorough and consistent assessment. Categorizing risks based on their type (e.g., financial, operational, strategic, legal, reputational), likelihood, and potential impact is essential for prioritization and resource allocation. For instance, risks might be categorized as high-frequency/low-severity (e.g., minor property damage) or low-frequency/high-severity (e.g., major product liability claim). Risk Evaluation and Quantification Once identified, each risk must be evaluated to determine its potential impact and likelihood. This often involves qualitative assessments, such as assigning risk scores based on expert judgment, and quantitative assessments, such as using historical loss data and statistical modeling. For example, a detailed analysis of past claims data can help quantify the frequency and severity of certain types of risks, such as workers’ compensation claims. This analysis will inform the captive’s underwriting decisions and the establishment of appropriate reserves. Risk Mitigation Strategies Following risk evaluation, appropriate mitigation strategies should be implemented. These strategies aim to reduce the likelihood or impact of identified risks. Examples include implementing improved safety protocols to reduce workplace accidents, investing in robust cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches, or purchasing reinsurance to cover catastrophic losses. The choice of mitigation strategy depends on the nature of the risk, its potential impact, and the cost-effectiveness of various options. A cost-benefit analysis should be conducted for each proposed mitigation strategy. Risk Monitoring and Review Regular monitoring and review of the captive’s risk profile is essential. This involves tracking key risk indicators (KRIs), analyzing emerging risks, and updating the risk assessment framework as needed. For example, the captive might monitor the frequency and severity of claims, the effectiveness of implemented mitigation strategies, and changes in the regulatory environment. Annual risk reviews, involving the captive’s management team and external experts, should be conducted to ensure the ongoing effectiveness of the risk management program. This review should also assess the adequacy of the captive’s reserves and reinsurance coverage. Any significant changes in the risk profile or the effectiveness of mitigation strategies should trigger an immediate reassessment and adjustments to the captive’s risk management plan. Regulatory Compliance and Legal Considerations Operating a United Group Captive Insurance requires meticulous adherence to a complex web of regulatory and legal frameworks. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Understanding these requirements is paramount to the success and longevity of the captive.Navigating the regulatory landscape necessitates a thorough understanding of the applicable laws and the responsibilities they impose on the captive insurer, its members, and its management. This includes understanding the licensing and registration processes, ongoing reporting obligations, and the specific requirements for financial solvency and operational transparency. Key Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Requirements The regulatory environment for group captives varies significantly depending on the jurisdiction in which the captive is domiciled. Common regulatory bodies include state insurance departments (in the U.S.), equivalent national insurance regulators in other countries, and potentially international bodies depending on the captive’s structure and operations. Compliance typically involves meeting stringent capital requirements, maintaining detailed records of financial transactions and risk assessments, undergoing regular audits, and adhering to specific insurance regulations concerning policy issuance, claims handling, and reinsurance arrangements. For example, in Vermont, the Department of Financial Regulation imposes rigorous standards for captive insurers, encompassing aspects such as financial reporting, risk management, and actuarial analysis. Similarly, other jurisdictions, such as Bermuda or the Cayman Islands, have their own established regulatory frameworks with specific compliance demands. Legal Implications of Operating a United Group Captive Insurance Establishing and operating a United Group Captive entails significant legal considerations. These include issues related to contract law, corporate governance, tax implications, and the potential for legal challenges from policyholders or other stakeholders. The legal structure of the captive, whether it’s a limited liability company (LLC), a corporation, or another entity, will impact its legal obligations and liabilities. Careful consideration must be given to the captive’s articles of incorporation, bylaws, and operating agreements to ensure compliance with relevant legal standards and to mitigate potential risks. For example, the choice of domicile significantly impacts tax implications and regulatory oversight. Selecting a jurisdiction known for its favorable regulatory environment and tax benefits is a critical strategic decision. Furthermore, the captive’s legal counsel should advise on all aspects of contract drafting, ensuring that policy language accurately reflects the intended risk transfer and complies with applicable insurance laws. Legal Documents and Procedures Checklist Maintaining a comprehensive set of legal documents and adhering to established procedures is crucial for regulatory compliance. This checklist is not exhaustive and should be supplemented by advice from legal and insurance professionals familiar with the specific jurisdiction and the captive’s structure. Articles of Incorporation/Formation Documents Bylaws/Operating Agreement … Read more