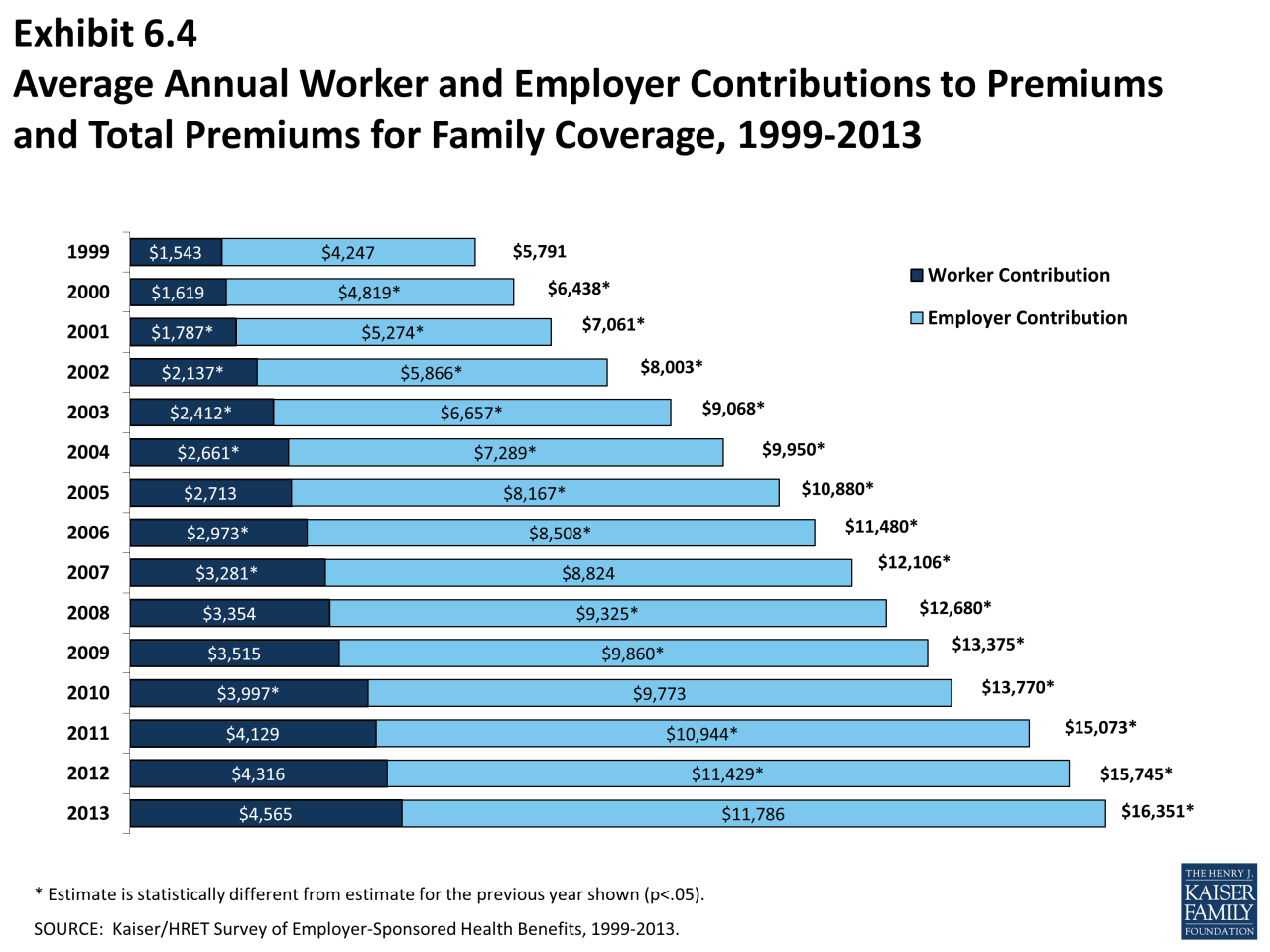
Decoding Health Insurance Costs: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the complex world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a foreign language, especially when it comes to understanding the often-confusing factors that determine your premiums. From age and health status to location and coverage options, a myriad of variables influence the cost of health insurance, making it a crucial aspect of financial planning. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricacies of health insurance costs, providing insights into the key factors that impact your premiums, exploring different plan types and their associated costs, and offering strategies for finding the most affordable coverage. We’ll delve into the nuances of health insurance, empowering you to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of this essential financial aspect. Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs Health insurance premiums are a significant expense for individuals and families. Understanding the factors that influence these costs is crucial for making informed decisions about coverage. Factors Determining Health Insurance Premiums Several key factors contribute to the cost of health insurance premiums. These factors include: Age: Older individuals tend to have higher healthcare costs due to a greater likelihood of chronic conditions and increased healthcare utilization. Therefore, health insurance premiums typically increase with age. Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a history of high healthcare utilization may face higher premiums. Insurers assess risk profiles to determine premium rates, factoring in health status as a significant element. Location: Geographic location plays a role in health insurance costs. Areas with higher concentrations of medical providers, higher cost of living, and greater demand for healthcare services tend to have higher premiums. Coverage Options: The type and level of coverage selected significantly influence premium costs. Comprehensive plans with broader coverage and lower deductibles generally have higher premiums compared to plans with limited coverage and higher deductibles. Age and Health Insurance Premiums Age is a significant factor influencing health insurance costs. As individuals age, they are more likely to experience health issues, leading to increased healthcare utilization. This higher risk profile translates into higher premiums for older individuals. For example, a 60-year-old individual may pay significantly more for health insurance than a 30-year-old individual with the same coverage. Health Status and Health Insurance Premiums An individual’s health status is another critical factor affecting health insurance premiums. Insurers assess risk profiles to determine premium rates, considering factors such as pre-existing conditions, medical history, and overall health. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a history of high healthcare utilization may face higher premiums due to their perceived higher risk. For instance, an individual with diabetes may pay a higher premium compared to an individual without any pre-existing conditions. Location and Health Insurance Premiums Geographic location plays a role in health insurance costs. Areas with higher concentrations of medical providers, higher cost of living, and greater demand for healthcare services tend to have higher premiums. The cost of medical care, including hospital stays, physician visits, and prescription drugs, can vary significantly based on location. For example, health insurance premiums in major metropolitan areas are generally higher than those in rural areas. Coverage Options and Health Insurance Premiums The type and level of coverage selected significantly influence premium costs. Comprehensive plans with broader coverage and lower deductibles generally have higher premiums compared to plans with limited coverage and higher deductibles. Individuals can choose from a variety of plans, including HMOs, PPOs, and EPOs, each with its own coverage features and cost structure. Comparing Health Insurance Plan Costs HMO (Health Maintenance Organization): HMOs typically have lower premiums than other types of plans. However, they often have restricted provider networks, requiring members to see in-network providers. PPO (Preferred Provider Organization): PPOs offer more flexibility in choosing providers, allowing members to see both in-network and out-of-network providers. However, they typically have higher premiums than HMOs. EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization): EPOs are similar to HMOs in that they require members to see in-network providers. However, they typically offer slightly higher premiums than HMOs but provide more flexibility in choosing providers within the network. Understanding Health Insurance Plans Navigating the world of health insurance can be confusing, with numerous plans and options available. Understanding the different types of plans and their key features is crucial for making informed decisions. Health Insurance Plan Types Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage and costs. Here’s a breakdown of common plan types: Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): HMO plans typically offer lower premiums but require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network. Referrals are usually required to see specialists. Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): PPO plans provide more flexibility, allowing you to see doctors both in and out of network. However, out-of-network care comes with higher costs. Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): EPO plans resemble HMOs but offer slightly more flexibility. They usually require you to stay within the network for care, but may allow out-of-network emergency services. Point of Service (POS): POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs, offering network access but with higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care. High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): HDHPs feature lower premiums but have higher deductibles, meaning you pay more out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in. These plans are often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA). Key Plan Features Understanding key plan features is essential for comparing costs and coverage: Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket before insurance coverage begins. Co-pay: A fixed amount you pay for each doctor visit, prescription, or other service. Co-insurance: A percentage of the cost you pay after meeting your deductible. Out-of-pocket maximum: The maximum amount you pay for covered medical expenses in a year, after which your insurance covers 100% of costs. Health Savings Account (HSA) An HSA is a tax-advantaged savings account specifically designed for individuals with HDHPs. Tax Benefits: Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. Cost Savings: HSAs can help you save money on healthcare expenses by allowing you to accumulate funds for future medical needs. Rollover: Unused funds in an HSA can be rolled over to the next year, providing long-term savings potential. Exploring Cost Comparison Tools Navigating the complex world of health insurance can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to finding the most affordable plan. Thankfully, a plethora of online tools and resources exist to simplify this process and empower individuals to make informed decisions. These platforms provide a comprehensive comparison of health insurance plans based on various factors, enabling users to identify the best option for their specific needs and budget. Health Insurance Cost Comparison Websites Numerous websites dedicated to comparing health insurance costs offer valuable services to consumers. These platforms typically allow users to input their personal information, such as location, age, and desired coverage, to generate personalized quotes from different insurance providers. eHealth: eHealth is a well-established platform that offers a wide range of health insurance plans from multiple providers. Users can compare plans based on factors like premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and network coverage. eHealth also provides educational resources and customer support to assist users throughout the process. HealthCompare: HealthCompare is another reputable website that facilitates the comparison of health insurance plans. It allows users to filter plans based on their preferences and provides detailed information about each plan, including coverage details, provider networks, and customer reviews. HealthCompare also offers a tool to estimate monthly premiums based on individual circumstances. Healthcare.gov: The official website of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), Healthcare.gov, serves as a comprehensive resource for health insurance information. It provides access to a marketplace where individuals can compare plans and enroll in coverage. Healthcare.gov offers subsidies and tax credits to eligible individuals and families to make coverage more affordable. Features and Benefits of Cost Comparison Websites Cost comparison websites offer a range of features and benefits that simplify the process of finding affordable health insurance. These features include: Personalized Quotes: These websites generate customized quotes based on individual factors, providing a realistic estimate of potential costs. … Read more