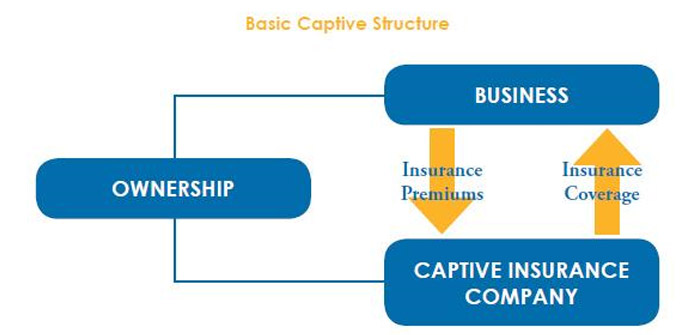
The complex world of risk management is constantly evolving, demanding innovative solutions for businesses seeking financial stability. Enter the United Group Captive Insurance model, a sophisticated approach that offers a compelling alternative to traditional insurance structures. This model allows a group of companies to pool their risks, creating a captive insurer owned and controlled by its members.
This shared ownership fosters transparency and allows for greater control over risk assessment, claims management, and ultimately, cost savings.
This in-depth analysis explores the intricacies of United Group Captive Insurance, examining its operational structure, regulatory landscape, and potential benefits. We’ll delve into risk management strategies tailored to this unique model, compare it to traditional insurance, and showcase successful implementations, highlighting key takeaways and future challenges.
Defining United Group Captive Insurance
United Group Captive Insurance represents a specialized form of insurance arrangement where a parent company, in this case, United Group, establishes its own insurance company to self-insure its risks. This differs significantly from traditional commercial insurance models, offering greater control and potential cost savings but also requiring substantial financial resources and expertise.This structure allows United Group to manage its risk profile more strategically, potentially reducing reliance on external insurers and improving transparency in its risk management processes.
The key differentiator lies in the ownership and control; unlike traditional insurance where a third party underwrites and manages risk, a captive insurer is wholly owned and operated by the parent company. This inherent control provides a unique level of flexibility in risk assessment and management.
Operational Structure and Governance
United Group Captive Insurance operates under a defined governance structure, typically overseen by a board of directors responsible for strategic decision-making and compliance. This board comprises individuals with significant experience in insurance, risk management, and finance. Day-to-day operations are managed by a team of experienced insurance professionals responsible for underwriting, claims management, and regulatory compliance.
The specific operational details and governance structure would be dictated by the jurisdiction in which the captive is domiciled and its internal policies. Robust internal controls and risk management frameworks are essential for the effective and compliant operation of such an entity.
Regular audits and compliance reviews are conducted to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and internal standards. Transparency and accountability are paramount to maintaining the integrity and financial stability of the captive insurance operation.
Benefits of a United Group Captive Insurance Structure
A United Group Captive Insurance structure offers a compelling alternative to traditional insurance arrangements, providing significant advantages in risk management, cost savings, and enhanced financial stability for participating companies. This structure leverages the collective risk pooling of multiple entities to achieve economies of scale and greater control over insurance costs and claims management.The primary benefit lies in the enhanced risk management capabilities it provides.
By pooling risks, the group mitigates the impact of individual losses, reducing the overall volatility of insurance costs. This proactive approach allows for more precise risk assessment and tailored coverage, addressing specific needs of the participating companies more effectively than standard, off-the-shelf policies.
Cost Savings Through Risk Pooling and Premium Negotiation
A key advantage of a United Group Captive is the potential for substantial cost savings. The pooling of risks allows for better premium negotiation with reinsurers, leading to lower overall insurance costs. Furthermore, the elimination of commissions and other intermediary fees common in traditional insurance models significantly reduces expenses.
For example, a group of five similarly sized construction companies might see a 15-20% reduction in their combined insurance premiums compared to purchasing individual policies. This cost savings can be reinvested into the businesses, boosting profitability and growth.
Enhanced Financial Stability Through Predictable Insurance Costs
The predictability of insurance costs is a significant contributor to the enhanced financial stability of participating companies. Unlike traditional insurance, where premiums can fluctuate significantly year to year based on market conditions and individual claims experience, a United Group Captive provides greater stability.
This predictable cost structure facilitates better financial planning and budgeting, reducing the risk of unexpected financial shocks. The shared risk also ensures that the financial burden of large claims is distributed across the group, preventing any single company from experiencing crippling losses.
This stability is particularly valuable in volatile economic climates or industries prone to significant risk events.
Improved Risk Management Practices and Loss Control
The shared ownership and governance structure of a United Group Captive incentivizes participating companies to actively improve their risk management practices. Through shared knowledge and experience, best practices are readily exchanged, leading to enhanced loss control measures across the group.
This collaborative approach fosters a culture of safety and risk mitigation, ultimately reducing the frequency and severity of claims, further enhancing cost savings and financial stability. For instance, a group of manufacturing companies might share safety protocols and training programs, leading to a demonstrable reduction in workplace accidents and associated insurance claims.
Risk Assessment and Management within the United Group Captive
Effective risk assessment and management are paramount for the success of any captive insurance program, particularly a United Group Captive. A robust framework ensures the captive remains financially sound and effectively protects the participating entities from unforeseen losses. This framework should be proactive, regularly reviewed, and adaptable to changing circumstances.
Risk Identification and Categorization
A comprehensive risk identification process is crucial. This involves systematically examining all potential risks faced by the member companies within the United Group. The process should be collaborative, involving risk managers from each member company and the captive’s management team.
A structured approach, using techniques such as brainstorming sessions, checklists, and risk surveys, helps ensure a thorough and consistent assessment. Categorizing risks based on their type (e.g., financial, operational, strategic, legal, reputational), likelihood, and potential impact is essential for prioritization and resource allocation.
For instance, risks might be categorized as high-frequency/low-severity (e.g., minor property damage) or low-frequency/high-severity (e.g., major product liability claim).
Risk Evaluation and Quantification
Once identified, each risk must be evaluated to determine its potential impact and likelihood. This often involves qualitative assessments, such as assigning risk scores based on expert judgment, and quantitative assessments, such as using historical loss data and statistical modeling.
For example, a detailed analysis of past claims data can help quantify the frequency and severity of certain types of risks, such as workers’ compensation claims. This analysis will inform the captive’s underwriting decisions and the establishment of appropriate reserves.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Following risk evaluation, appropriate mitigation strategies should be implemented. These strategies aim to reduce the likelihood or impact of identified risks. Examples include implementing improved safety protocols to reduce workplace accidents, investing in robust cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches, or purchasing reinsurance to cover catastrophic losses.
The choice of mitigation strategy depends on the nature of the risk, its potential impact, and the cost-effectiveness of various options. A cost-benefit analysis should be conducted for each proposed mitigation strategy.
Risk Monitoring and Review
Regular monitoring and review of the captive’s risk profile is essential. This involves tracking key risk indicators (KRIs), analyzing emerging risks, and updating the risk assessment framework as needed. For example, the captive might monitor the frequency and severity of claims, the effectiveness of implemented mitigation strategies, and changes in the regulatory environment.
Annual risk reviews, involving the captive’s management team and external experts, should be conducted to ensure the ongoing effectiveness of the risk management program. This review should also assess the adequacy of the captive’s reserves and reinsurance coverage.
Any significant changes in the risk profile or the effectiveness of mitigation strategies should trigger an immediate reassessment and adjustments to the captive’s risk management plan.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Considerations
Operating a United Group Captive Insurance requires meticulous adherence to a complex web of regulatory and legal frameworks. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Understanding these requirements is paramount to the success and longevity of the captive.Navigating the regulatory landscape necessitates a thorough understanding of the applicable laws and the responsibilities they impose on the captive insurer, its members, and its management.
This includes understanding the licensing and registration processes, ongoing reporting obligations, and the specific requirements for financial solvency and operational transparency.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory environment for group captives varies significantly depending on the jurisdiction in which the captive is domiciled. Common regulatory bodies include state insurance departments (in the U.S.), equivalent national insurance regulators in other countries, and potentially international bodies depending on the captive’s structure and operations.
Compliance typically involves meeting stringent capital requirements, maintaining detailed records of financial transactions and risk assessments, undergoing regular audits, and adhering to specific insurance regulations concerning policy issuance, claims handling, and reinsurance arrangements. For example, in Vermont, the Department of Financial Regulation imposes rigorous standards for captive insurers, encompassing aspects such as financial reporting, risk management, and actuarial analysis.
Similarly, other jurisdictions, such as Bermuda or the Cayman Islands, have their own established regulatory frameworks with specific compliance demands.
Legal Implications of Operating a United Group Captive Insurance
Establishing and operating a United Group Captive entails significant legal considerations. These include issues related to contract law, corporate governance, tax implications, and the potential for legal challenges from policyholders or other stakeholders. The legal structure of the captive, whether it’s a limited liability company (LLC), a corporation, or another entity, will impact its legal obligations and liabilities.
Careful consideration must be given to the captive’s articles of incorporation, bylaws, and operating agreements to ensure compliance with relevant legal standards and to mitigate potential risks. For example, the choice of domicile significantly impacts tax implications and regulatory oversight.
Selecting a jurisdiction known for its favorable regulatory environment and tax benefits is a critical strategic decision. Furthermore, the captive’s legal counsel should advise on all aspects of contract drafting, ensuring that policy language accurately reflects the intended risk transfer and complies with applicable insurance laws.
Legal Documents and Procedures Checklist
Maintaining a comprehensive set of legal documents and adhering to established procedures is crucial for regulatory compliance. This checklist is not exhaustive and should be supplemented by advice from legal and insurance professionals familiar with the specific jurisdiction and the captive’s structure.
- Articles of Incorporation/Formation Documents
- Bylaws/Operating Agreement
- Insurance License and Certificates of Authority
- Policy Forms and Endorsements
- Reinsurance Agreements
- Actuarial Reports and Financial Statements
- Risk Management Plan
- Claims Handling Procedures
- Compliance Manual
- Board Meeting Minutes
Claims Management Process within the United Group Captive
Efficient claims management is crucial for the financial stability and reputation of any captive insurance program. A well-defined process ensures timely and equitable resolution of claims, minimizing disruption to member companies and maintaining the integrity of the captive’s risk pool.
The United Group Captive prioritizes a transparent and streamlined approach to claims handling, focusing on prompt investigation, fair assessment, and efficient resolution.The claims management process begins with the initial notification of a claim. This notification, typically submitted through a designated online portal or directly to the claims administrator, triggers a series of pre-defined steps designed to gather all necessary information and assess the validity and extent of the claim.
The process involves thorough documentation, investigation, and communication with all involved parties to ensure accuracy and transparency throughout.
Claim Intake and Initial Assessment
Upon receipt of a claim, the assigned claims adjuster immediately reviews the documentation provided by the member company. This initial assessment involves verifying the completeness of the submitted information and identifying any potential discrepancies or missing data. The adjuster then initiates contact with the member company to clarify any ambiguities and gather any additional information required for a comprehensive assessment.
This stage prioritizes clear communication and prompt feedback to the claimant.
Investigation and Verification
Following the initial assessment, a thorough investigation is undertaken to verify the validity of the claim. This may involve reviewing relevant contracts, policies, and supporting documentation, conducting interviews with witnesses or involved parties, and potentially engaging external experts for specialized assessments, such as engineers for property damage claims or medical professionals for liability claims.
The goal is to gather sufficient evidence to accurately determine the extent of the loss and the insurer’s liability. For example, a claim involving a data breach would necessitate a detailed forensic investigation to ascertain the extent of the breach and resulting damages.
Claim Evaluation and Negotiation
Once the investigation is complete, the claims adjuster evaluates the claim based on the gathered evidence and applicable policy terms. This evaluation involves determining the extent of the insurer’s liability and calculating the appropriate indemnity payment. In cases where the claim amount is disputed, the adjuster engages in negotiation with the member company to reach a mutually acceptable settlement.
This process emphasizes collaborative problem-solving and aims to achieve a fair and equitable outcome for all parties involved. For instance, a disagreement on the valuation of damaged equipment might require appraisal by an independent expert.
Claim Resolution and Payment
Upon reaching an agreement on the claim amount, the claims adjuster prepares the necessary documentation for payment processing. This involves finalizing the claim file and ensuring all necessary approvals have been obtained. Once approved, the payment is processed and disbursed to the member company in accordance with the agreed-upon terms.
The entire process is meticulously documented, maintaining a clear audit trail for transparency and accountability. In situations involving complex legal considerations, external legal counsel may be consulted to ensure compliance with all relevant regulations.
Dispute Resolution Procedures
In the event that a dispute arises that cannot be resolved through negotiation, the United Group Captive has established a formal dispute resolution process. This process may involve internal review by senior claims personnel or, if necessary, arbitration or litigation.
The specific procedures followed depend on the nature and complexity of the dispute, but the overarching goal remains to achieve a fair and equitable resolution while minimizing disruption and maintaining the integrity of the captive’s risk pool. This process adheres to established legal frameworks and industry best practices.
Claim Management Workflow
The following table illustrates the workflow for claim management within the United Group Captive:
| Claim Number | Date Received | Status | Assigned Adjuster |
|---|---|---|---|
| CG2023-101 | 2023-10-26 | Pending Investigation | John Smith |
| CG2023-102 | 2023-11-15 | Under Review | Jane Doe |
| CG2023-103 | 2023-12-01 | Settled | John Smith |
| CG2023-104 | 2023-12-10 | Awaiting Documentation | Jane Doe |
Financial Reporting and Transparency
The financial health and stability of a captive insurance company, such as the United Group Captive, are paramount for its long-term success and the confidence of its parent companies. A robust and transparent financial reporting structure is essential not only for regulatory compliance but also for effective risk management and strategic decision-making.
This section Artikels a suitable framework for financial reporting and emphasizes the critical role of transparency in maintaining the integrity of the captive’s operations.A well-designed financial reporting structure for the United Group Captive should adhere to accepted accounting principles, providing a clear and comprehensive picture of its financial position, performance, and cash flows.
This requires a structured approach encompassing regular reporting cycles, detailed financial statements, and appropriate internal controls. The system should be designed to facilitate both internal monitoring and external audits, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the reported information.
Financial Reporting Structure
The United Group Captive should adopt a financial reporting structure aligned with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), depending on its jurisdiction. This involves the preparation of regular financial statements, including a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
These statements should be prepared at least annually, and more frequently if required by regulators or internal management needs. Furthermore, a comprehensive actuarial analysis should be conducted periodically to assess the adequacy of reserves and the overall financial strength of the captive.
This analysis should account for factors such as claims experience, investment returns, and projected future liabilities. The reports should be clearly presented, easily understandable, and include supporting schedules and notes that provide sufficient detail to allow stakeholders to fully understand the captive’s financial position.
Internal controls, such as segregation of duties and regular reconciliation procedures, should be implemented to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the financial data.
Importance of Transparency in Financial Reporting
Transparency in financial reporting is crucial for building trust and confidence among stakeholders, including the parent companies, regulators, and auditors. Open and honest communication regarding the captive’s financial performance and risk profile allows for informed decision-making and proactive risk management.
Lack of transparency can lead to mistrust, regulatory scrutiny, and potential legal challenges. A transparent reporting process ensures that all relevant information is readily available to those who need it, facilitating effective oversight and accountability. Transparency also promotes efficient capital allocation within the group, as parent companies can accurately assess the captive’s contribution to the overall risk management strategy.
For example, clear reporting on investment performance and claims experience allows for better forecasting and budgeting.
Methods for Ensuring Accurate and Reliable Financial Reporting
Several methods can be employed to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting within the United Group Captive. These include the implementation of robust internal controls, the engagement of independent auditors, and the use of sophisticated accounting software.
Internal controls should encompass segregation of duties, regular reconciliation of accounts, and a strong system of checks and balances. Independent audits provide an external verification of the financial statements, enhancing the credibility and reliability of the reported information.
Sophisticated accounting software can automate many aspects of the financial reporting process, reducing the risk of human error and improving efficiency. Regular training for accounting staff on the latest accounting standards and best practices is essential to maintain a high level of competence and adherence to professional standards.
Furthermore, the establishment of a clear reporting structure with well-defined roles and responsibilities helps to streamline the process and minimize the risk of errors or omissions. Regular reviews of the financial reporting system should be undertaken to identify areas for improvement and to ensure that the system remains effective and efficient.
Comparison with Traditional Insurance Models
United Group Captive Insurance presents a distinct alternative to traditional insurance models, offering a nuanced approach to risk management that necessitates a careful comparison to understand its suitability for various organizations. Both approaches aim to mitigate financial losses from unforeseen events, but they differ significantly in their structure, control, and cost implications.Traditional insurance involves purchasing policies from commercial insurers who pool risks from numerous unrelated entities.
This model offers simplicity and readily available coverage, but it often comes with higher premiums and less control over claims processes. In contrast, a United Group Captive allows a group of companies to self-insure, sharing risks and potentially reducing overall costs.
Cost Comparison
The cost structure of a United Group Captive versus traditional insurance is a key differentiator. Traditional insurance premiums are determined by actuarial assessments of risk, often incorporating industry benchmarks and historical loss data. These premiums can be substantial, especially for businesses with high-risk profiles.
A United Group Captive, conversely, aims to reduce costs by eliminating profit margins and administrative expenses associated with commercial insurers. Savings are realized through the pooling of resources and internal management of claims. However, upfront costs for establishing and maintaining the captive, including legal and administrative fees, must be considered.
The long-term cost-effectiveness will depend on the group’s claims experience and the overall risk profile. For example, a group with a consistent history of low claims may realize significant savings compared to the premiums paid to traditional insurers.
Control and Risk Management
A significant advantage of a United Group Captive is the enhanced control it affords over risk management and claims processes. Traditional insurance typically involves limited input from the policyholder in these areas. The insurer sets the terms, manages claims, and determines payouts.
In contrast, a United Group Captive allows member companies to actively participate in risk assessment, loss control programs, and claims handling. This participatory approach fosters a more proactive risk management culture and allows for greater customization of coverage to meet specific needs.
For instance, the group can tailor its insurance program to cover specific risks that might be excluded or inadequately addressed by traditional policies.
Suitability of a United Group Captive
A United Group Captive is most suitable for groups of companies with similar risk profiles, significant insurable exposures, and a commitment to proactive risk management. The optimal size of the group will depend on the nature and volume of risks involved, but a critical mass is needed to effectively pool risks and achieve cost savings.
Companies with consistently high claims experience might not benefit from this structure, as the potential cost savings might be offset by increased claims payouts. Furthermore, the group’s ability to effectively manage risk and comply with regulatory requirements is crucial for the success of a United Group Captive.
Groups with sophisticated risk management capabilities and a strong commitment to compliance are more likely to find this structure advantageous.
Case Studies of Successful United Group Captives
The effectiveness of a United Group Captive insurance structure is best illustrated through real-world examples. Examining successful implementations reveals key strategies and highlights crucial lessons for organizations considering this approach to risk management. The following case studies showcase diverse industries and demonstrate the adaptability of this model.
Successful Implementation in the Manufacturing Sector
A consortium of five mid-sized manufacturing companies, operating across various states, formed a United Group Captive. Facing escalating workers’ compensation premiums and inconsistent coverage, they pooled their risks and leveraged their combined purchasing power to negotiate favorable reinsurance terms.
This resulted in a significant reduction in overall insurance costs and improved risk management capabilities through shared expertise and best practices. The key to their success was the strong collaborative relationship between the member companies, facilitated by a dedicated captive management team.
This team provided expertise in claims management, risk assessment, and regulatory compliance.
A Case Study in the Healthcare Industry
A group of ten regional healthcare providers established a United Group Captive to address the increasing frequency and severity of medical malpractice claims. By pooling their risks, they achieved greater predictability in their insurance costs and gained access to specialized risk management resources.
Their success stemmed from a robust risk assessment program implemented across all member organizations, allowing for proactive identification and mitigation of potential liabilities. This proactive approach, coupled with rigorous claims management, minimized losses and fostered a culture of risk awareness within each participating healthcare facility.
Key Factors Contributing to Success
The success of these and other United Group Captives hinges on several critical factors. A well-defined governance structure, transparent communication, and a commitment to shared risk management principles are essential. The selection of a competent captive manager is also crucial, as they play a vital role in overseeing the day-to-day operations and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Furthermore, the ability to accurately assess and manage risks across the group is paramount. This requires robust data collection and analysis, along with the implementation of effective risk mitigation strategies.
Lessons Learned from Successful Implementations
The experiences of successful United Group Captives offer valuable lessons for organizations considering this model.
- Thorough due diligence is critical before forming a captive. This includes a comprehensive risk assessment, careful selection of member companies, and a detailed evaluation of the legal and regulatory landscape.
- Establishing a strong governance structure with clear roles and responsibilities is crucial for effective decision-making and oversight.
- Transparent communication and collaboration among member companies are essential for building trust and ensuring the long-term success of the captive.
- Investing in a skilled captive management team is vital for efficient operations and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Regular review and evaluation of the captive’s performance are necessary to identify areas for improvement and adapt to changing circumstances.
Future Trends and Challenges for United Group Captives
The landscape of United Group Captive Insurance is poised for significant transformation, driven by evolving risk profiles, technological advancements, and regulatory shifts. Understanding these emerging trends and proactively addressing potential challenges is crucial for maintaining the viability and competitiveness of this increasingly popular risk management strategy.The future of United Group Captives will be shaped by a confluence of factors, demanding strategic adaptation from both insurers and their members.
These factors range from the increasing complexity of global risks to the accelerating pace of technological innovation. Failure to adapt could result in diminished effectiveness and potential market displacement.
Emerging Trends in United Group Captive Insurance
Several key trends are reshaping the United Group Captive landscape. The increasing prevalence of cyber risks, for instance, necessitates specialized risk assessment and mitigation strategies within the captive structure. Simultaneously, the growing adoption of Insurtech solutions offers opportunities for enhanced efficiency and data-driven decision-making in claims management and risk profiling.
Furthermore, the rise of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing is influencing the investment strategies of many captives, pushing for greater transparency and alignment with sustainable practices. Finally, the ongoing globalization of business operations requires captives to navigate increasingly complex international regulatory frameworks.
Challenges Facing United Group Captives
The future of United Group Captives is not without its challenges. One significant hurdle is the potential for increased regulatory scrutiny, particularly in the areas of solvency and transparency. This requires proactive engagement with regulators and the implementation of robust compliance programs.
Another challenge is the need for continuous adaptation to evolving risk landscapes. Emerging risks, such as those related to climate change and pandemics, require innovative risk management strategies and diversification within the captive’s portfolio. Finally, the increasing competition from traditional insurers and other alternative risk transfer mechanisms demands a focus on cost-effectiveness and value-added services.
Strategies for Adaptation and Maintaining Competitiveness
To navigate these challenges and maintain competitiveness, United Group Captives must prioritize several key strategies. This includes investing in advanced analytics and technology to improve risk assessment and claims management, fostering strong relationships with regulators to ensure compliance, and actively seeking opportunities for diversification and innovation within their investment portfolios.
Moreover, a proactive approach to risk identification and mitigation, including scenario planning for emerging risks, is essential. Finally, enhancing transparency and communication with members is crucial for building trust and maintaining the long-term viability of the captive structure.
A Potential Future Scenario: The Year 2030
Imagine the year A major multinational corporation, ”GlobalTech,” operates a sophisticated United Group Captive. Their captive utilizes AI-powered risk assessment tools to identify and mitigate emerging cyber threats, including sophisticated ransomware attacks and data breaches. GlobalTech’s captive has also diversified its investment portfolio to include sustainable infrastructure projects, aligning with their ESG commitments.
However, they face new challenges: a significant regulatory shift in a key operating region requires a substantial overhaul of their compliance procedures. Simultaneously, a sudden global supply chain disruption caused by a major geopolitical event forces the captive to rapidly re-evaluate its risk profile and adjust its reinsurance strategy.
The success of GlobalTech’s captive in 2030 will depend on its agility in adapting to these dynamic changes, leveraging technology, and maintaining strong relationships with its members and regulators.
Last Recap
United Group Captive Insurance presents a powerful tool for businesses seeking enhanced risk management and cost-effective insurance solutions. By fostering collaboration, transparency, and proactive risk mitigation, this model empowers participating companies to achieve greater financial stability. While regulatory compliance and careful risk assessment are paramount, the potential benefits—including reduced premiums, improved claims management, and enhanced control—make it a compelling option for the right group of companies.
As the insurance landscape continues to evolve, the United Group Captive model is poised to play an increasingly significant role in protecting businesses against unforeseen risks.