Navigating the complex world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a foreign language, especially when it comes to understanding the often-confusing factors that determine your premiums. From age and health status to location and coverage options, a myriad of variables influence the cost of health insurance, making it a crucial aspect of financial planning.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricacies of health insurance costs, providing insights into the key factors that impact your premiums, exploring different plan types and their associated costs, and offering strategies for finding the most affordable coverage. We’ll delve into the nuances of health insurance, empowering you to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of this essential financial aspect.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
Health insurance premiums are a significant expense for individuals and families. Understanding the factors that influence these costs is crucial for making informed decisions about coverage.
Factors Determining Health Insurance Premiums
Several key factors contribute to the cost of health insurance premiums. These factors include:
- Age: Older individuals tend to have higher healthcare costs due to a greater likelihood of chronic conditions and increased healthcare utilization. Therefore, health insurance premiums typically increase with age.
- Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a history of high healthcare utilization may face higher premiums. Insurers assess risk profiles to determine premium rates, factoring in health status as a significant element.
- Location: Geographic location plays a role in health insurance costs. Areas with higher concentrations of medical providers, higher cost of living, and greater demand for healthcare services tend to have higher premiums.
- Coverage Options: The type and level of coverage selected significantly influence premium costs. Comprehensive plans with broader coverage and lower deductibles generally have higher premiums compared to plans with limited coverage and higher deductibles.
Age and Health Insurance Premiums
Age is a significant factor influencing health insurance costs. As individuals age, they are more likely to experience health issues, leading to increased healthcare utilization. This higher risk profile translates into higher premiums for older individuals.
For example, a 60-year-old individual may pay significantly more for health insurance than a 30-year-old individual with the same coverage.
Health Status and Health Insurance Premiums
An individual’s health status is another critical factor affecting health insurance premiums. Insurers assess risk profiles to determine premium rates, considering factors such as pre-existing conditions, medical history, and overall health. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a history of high healthcare utilization may face higher premiums due to their perceived higher risk.
For instance, an individual with diabetes may pay a higher premium compared to an individual without any pre-existing conditions.
Location and Health Insurance Premiums
Geographic location plays a role in health insurance costs. Areas with higher concentrations of medical providers, higher cost of living, and greater demand for healthcare services tend to have higher premiums. The cost of medical care, including hospital stays, physician visits, and prescription drugs, can vary significantly based on location.
For example, health insurance premiums in major metropolitan areas are generally higher than those in rural areas.
Coverage Options and Health Insurance Premiums
The type and level of coverage selected significantly influence premium costs. Comprehensive plans with broader coverage and lower deductibles generally have higher premiums compared to plans with limited coverage and higher deductibles. Individuals can choose from a variety of plans, including HMOs, PPOs, and EPOs, each with its own coverage features and cost structure.
Comparing Health Insurance Plan Costs
- HMO (Health Maintenance Organization): HMOs typically have lower premiums than other types of plans. However, they often have restricted provider networks, requiring members to see in-network providers.
- PPO (Preferred Provider Organization): PPOs offer more flexibility in choosing providers, allowing members to see both in-network and out-of-network providers. However, they typically have higher premiums than HMOs.
- EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization): EPOs are similar to HMOs in that they require members to see in-network providers. However, they typically offer slightly higher premiums than HMOs but provide more flexibility in choosing providers within the network.
Understanding Health Insurance Plans
Navigating the world of health insurance can be confusing, with numerous plans and options available. Understanding the different types of plans and their key features is crucial for making informed decisions.
Health Insurance Plan Types
Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage and costs. Here’s a breakdown of common plan types:
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): HMO plans typically offer lower premiums but require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network. Referrals are usually required to see specialists.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): PPO plans provide more flexibility, allowing you to see doctors both in and out of network. However, out-of-network care comes with higher costs.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): EPO plans resemble HMOs but offer slightly more flexibility. They usually require you to stay within the network for care, but may allow out-of-network emergency services.
- Point of Service (POS): POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs, offering network access but with higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care.
- High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): HDHPs feature lower premiums but have higher deductibles, meaning you pay more out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in. These plans are often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA).
Key Plan Features
Understanding key plan features is essential for comparing costs and coverage:
- Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket before insurance coverage begins.
- Co-pay: A fixed amount you pay for each doctor visit, prescription, or other service.
- Co-insurance: A percentage of the cost you pay after meeting your deductible.
- Out-of-pocket maximum: The maximum amount you pay for covered medical expenses in a year, after which your insurance covers 100% of costs.
Health Savings Account (HSA)
An HSA is a tax-advantaged savings account specifically designed for individuals with HDHPs.
- Tax Benefits: Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
- Cost Savings: HSAs can help you save money on healthcare expenses by allowing you to accumulate funds for future medical needs.
- Rollover: Unused funds in an HSA can be rolled over to the next year, providing long-term savings potential.
Exploring Cost Comparison Tools
Navigating the complex world of health insurance can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to finding the most affordable plan. Thankfully, a plethora of online tools and resources exist to simplify this process and empower individuals to make informed decisions. These platforms provide a comprehensive comparison of health insurance plans based on various factors, enabling users to identify the best option for their specific needs and budget.
Health Insurance Cost Comparison Websites
Numerous websites dedicated to comparing health insurance costs offer valuable services to consumers. These platforms typically allow users to input their personal information, such as location, age, and desired coverage, to generate personalized quotes from different insurance providers.
- eHealth: eHealth is a well-established platform that offers a wide range of health insurance plans from multiple providers. Users can compare plans based on factors like premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and network coverage. eHealth also provides educational resources and customer support to assist users throughout the process.
- HealthCompare: HealthCompare is another reputable website that facilitates the comparison of health insurance plans. It allows users to filter plans based on their preferences and provides detailed information about each plan, including coverage details, provider networks, and customer reviews. HealthCompare also offers a tool to estimate monthly premiums based on individual circumstances.
- Healthcare.gov: The official website of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), Healthcare.gov, serves as a comprehensive resource for health insurance information. It provides access to a marketplace where individuals can compare plans and enroll in coverage. Healthcare.gov offers subsidies and tax credits to eligible individuals and families to make coverage more affordable.
Features and Benefits of Cost Comparison Websites
Cost comparison websites offer a range of features and benefits that simplify the process of finding affordable health insurance. These features include:
- Personalized Quotes: These websites generate customized quotes based on individual factors, providing a realistic estimate of potential costs.
- Plan Comparisons: Users can compare plans side-by-side, highlighting key differences in coverage, premiums, deductibles, and other factors.
- Filter Options: Advanced filtering options allow users to narrow down their search based on specific criteria, such as desired coverage, provider network, and budget.
- Educational Resources: Many websites provide educational content to help users understand health insurance terminology, coverage options, and enrollment processes.
- Customer Support: Dedicated customer support teams are available to answer questions and assist users with the enrollment process.
Using Cost Comparison Tools Effectively
To maximize the effectiveness of health insurance cost comparison tools, individuals should follow these steps:
- Gather Essential Information: Before using any comparison tool, gather necessary information, including location, age, income, desired coverage, and any pre-existing health conditions. This information will ensure accurate and personalized quotes.
- Explore Multiple Websites: Comparing quotes from different websites can provide a broader perspective and help identify the most competitive plans.
- Read Plan Details Carefully: Pay close attention to the details of each plan, including coverage limits, deductibles, co-pays, and provider networks. Ensure the plan meets individual needs and budget constraints.
- Consider Long-Term Costs: Evaluate the potential for future cost increases and factor in the long-term implications of choosing a particular plan.
- Contact Insurance Providers: If necessary, contact insurance providers directly to clarify any questions or obtain additional information.
Navigating the Open Enrollment Period
The open enrollment period (OEP) is a crucial time for individuals and families to review their health insurance needs and make adjustments to their coverage. During this limited window, you can enroll in, change, or cancel your health insurance plan. Understanding the significance of the OEP and navigating the enrollment process effectively can ensure you have the right coverage for your needs and budget.
Key Steps in Choosing and Enrolling in a Health Insurance Plan
During the OEP, it’s essential to take deliberate steps to choose and enroll in a health insurance plan that aligns with your healthcare needs and financial situation.
- Assess your healthcare needs: Consider your current health status, anticipated healthcare needs for the upcoming year, and any pre-existing conditions you may have. This will help you determine the level of coverage and benefits you require.
- Compare plans: Utilize online marketplaces, insurance company websites, or a broker to compare various plans offered in your area. Consider factors such as premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coverage for essential services like preventive care, prescription drugs, and hospitalization.
- Review plan details: Carefully read the plan documents, including the Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC), to understand the specifics of coverage, benefits, and cost-sharing arrangements.
- Choose a plan: Select the plan that best meets your healthcare needs and budget. Be sure to consider your overall health status, anticipated healthcare expenses, and financial capabilities.
- Enroll in the plan: Complete the enrollment process through the chosen marketplace or insurance company website. Provide all required information and confirm your enrollment details.
Tips for Making Informed Decisions
Making informed decisions during the OEP is crucial to ensure you have the right coverage.
- Start early: Don’t wait until the last minute to review your options. Begin researching plans and comparing options well in advance of the OEP deadline.
- Seek guidance: If you find the process overwhelming, consider consulting a health insurance broker or navigator for assistance. They can provide personalized guidance and help you choose the best plan for your needs.
- Understand your options: Familiarize yourself with the different types of health insurance plans available, including Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs).
- Factor in out-of-pocket costs: Beyond premiums, consider out-of-pocket expenses such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. These costs can vary significantly between plans and can impact your overall healthcare expenses.
- Check for network coverage: Ensure your preferred doctors, hospitals, and pharmacies are included in the plan’s network. Out-of-network care can be significantly more expensive.
Avoiding Common Enrollment Mistakes
To avoid common enrollment mistakes, it’s important to be aware of potential pitfalls and take steps to mitigate them.
- Missing the deadline: The OEP has a specific enrollment period. Ensure you complete the enrollment process before the deadline to avoid a gap in coverage.
- Choosing a plan based solely on price: While premiums are important, don’t base your decision solely on cost. Consider the overall value of the plan, including coverage for essential services and out-of-pocket costs.
- Not reading the plan details: Don’t skip over the fine print. Carefully review the plan documents to understand the specifics of coverage, benefits, and cost-sharing arrangements.
- Not updating your contact information: Ensure your contact information is up-to-date with your insurance company to receive important notices and updates.
Government Subsidies and Financial Assistance
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has made health insurance more accessible and affordable for millions of Americans by offering government subsidies and financial assistance to help offset the cost of premiums. These programs are designed to reduce the financial burden of healthcare and ensure that individuals and families have access to quality healthcare.
Eligibility Criteria for Subsidies
Eligibility for government subsidies is determined based on several factors, including income, household size, and location. The ACA’s premium tax credits are available to individuals and families with incomes below certain thresholds. The amount of the subsidy is determined by a sliding scale, with higher subsidies available to those with lower incomes. To qualify for subsidies, individuals must:
- Be a U.S. citizen or a lawful permanent resident.
- Not be incarcerated.
- Not be eligible for Medicare.
- Not be covered by employer-sponsored health insurance.
Application Process for Financial Assistance
Individuals can apply for subsidies through the Health Insurance Marketplace, also known as the ACA Marketplace. The application process involves providing information about income, household size, and other relevant factors. The Marketplace will then determine eligibility for subsidies and provide a list of available health insurance plans with estimated monthly premiums.
Impact of Subsidies on Health Insurance Costs
Government subsidies have a significant impact on the overall cost of health insurance. They can significantly reduce the monthly premiums individuals and families have to pay, making health insurance more affordable. For example, a family of four with an annual income of $50,000 could receive a substantial subsidy that reduces their monthly premium by hundreds of dollars.
“The average premium tax credit for individuals and families in 2023 is estimated to be around $700 per month.”
This reduction in premiums can have a significant impact on household budgets, allowing individuals and families to allocate more of their income to other essential expenses.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Employer-sponsored health insurance is a common way for Americans to obtain health coverage. This type of insurance is offered by an employer to their employees, and it can provide a variety of benefits, such as access to a network of healthcare providers, prescription drug coverage, and preventive care services.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Employer-sponsored health insurance offers several advantages. For example, it can be more affordable than individual health insurance plans, as employers often negotiate lower premiums with insurance companies. In addition, employer-sponsored plans may offer a wider range of benefits and coverage options than individual plans.
However, there are also some drawbacks to employer-sponsored health insurance. For example, coverage is tied to employment, meaning that employees may lose their health insurance if they lose their jobs. Additionally, the availability of different plans and coverage options can vary from employer to employer.
Cost Comparison with Individual Health Insurance Plans
The cost of employer-sponsored health insurance can vary depending on a number of factors, including the size of the employer, the location of the business, and the type of coverage offered. However, employer-sponsored plans are generally less expensive than individual health insurance plans.
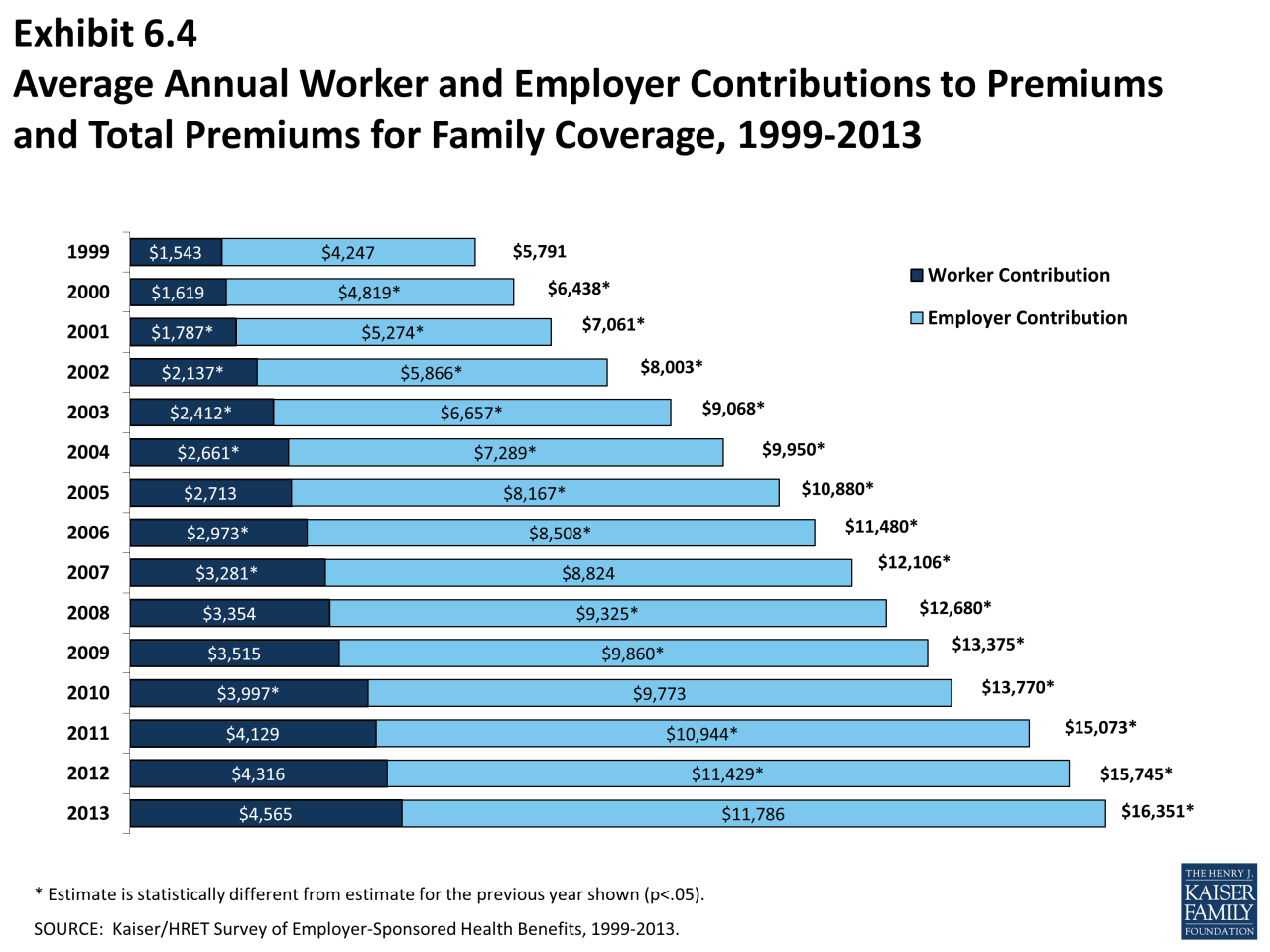
According to a 2022 study by the Kaiser Family Foundation, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored health insurance was $7,739 for single coverage and $22,221 for family coverage. In contrast, the average annual premium for individual health insurance plans purchased through the Affordable Care Act marketplaces was $5,200 for single coverage and $13,400 for family coverage.
Factors Employers Consider When Choosing Health Insurance Plans
Employers consider several factors when choosing health insurance plans for their employees. These factors include:
- The cost of the plan: Employers want to offer affordable health insurance to their employees, but they also need to ensure that the plan is financially sustainable for their business.
- The benefits offered: Employers want to choose a plan that offers comprehensive coverage, including preventive care, prescription drug coverage, and mental health services.
- The network of healthcare providers: Employers want to ensure that their employees have access to a wide network of healthcare providers, including doctors, hospitals, and specialists.
- The satisfaction of employees: Employers want to choose a plan that is well-received by their employees.
Health Insurance for Small Businesses
Providing health insurance for employees is a significant challenge for small businesses, particularly given the complexities and costs associated with it. However, offering health insurance can be a powerful tool for attracting and retaining talent, boosting employee morale, and improving overall productivity. This section explores the unique challenges faced by small businesses and provides guidance on navigating the options available.
Group Health Plans
Small businesses with a limited number of employees may find it difficult to access affordable group health plans. Group plans often require a minimum number of employees to be eligible, and premiums can be higher than those offered to larger companies. However, there are several resources available to help small businesses find group health plans that fit their needs. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has expanded access to group health plans for small businesses, and several state and federal programs offer subsidies and tax credits to make coverage more affordable.
- Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP): This ACA marketplace allows small businesses with 50 or fewer employees to compare and purchase health insurance plans from multiple insurers. SHOP plans offer a range of coverage options, and businesses can choose a plan that best suits their budget and employee needs.
- Association Health Plans (AHPs): These plans allow small businesses to pool together with other businesses to form a larger group, which can lead to lower premiums and more competitive rates. AHPs are available in some states, and the rules governing them vary. Small businesses should research whether AHPs are an option in their state and carefully consider the pros and cons before joining.
Individual Coverage
Small businesses may also consider offering individual health insurance plans to their employees. Individual plans are purchased directly from an insurance company, and employees are responsible for choosing and paying for their own coverage. This option can provide flexibility and allow employees to select a plan that meets their individual needs. However, individual plans can be more expensive than group plans, and employees may face higher deductibles and out-of-pocket costs.
- Health Insurance Marketplace: The ACA marketplace offers individual health insurance plans to individuals and families, and small businesses can encourage their employees to explore this option. The marketplace offers a variety of plans, and individuals can receive subsidies to help offset the cost of coverage. Small businesses can also provide employees with resources and information about the marketplace to help them navigate the enrollment process.
- Direct-to-Consumer Plans: Several insurance companies offer individual health insurance plans directly to consumers. These plans may be more affordable than traditional individual plans, but it’s important for small businesses to encourage employees to carefully compare plans and ensure they are choosing coverage that meets their needs.
Resources for Small Businesses
Several resources are available to help small businesses navigate the complexities of providing health insurance to their employees. The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers guidance on health insurance options for small businesses, including information on the ACA, SHOP, and other programs. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) also provides resources on health insurance for small businesses, including information on enrollment deadlines, subsidies, and tax credits. Additionally, several private organizations offer assistance to small businesses, such as the National Small Business Association (NSBA) and the National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB).
- Small Business Administration (SBA): The SBA provides a wealth of information and resources for small businesses, including guidance on health insurance options, eligibility for tax credits, and assistance with navigating the ACA marketplace. The SBA also offers workshops and webinars on health insurance for small businesses.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS): The HHS provides information on health insurance options for small businesses, including the ACA, SHOP, and other programs. The HHS also offers resources on enrollment deadlines, subsidies, and tax credits.
- National Small Business Association (NSBA): The NSBA provides resources and advocacy for small businesses, including information on health insurance options and access to affordable coverage. The NSBA also offers workshops and webinars on health insurance for small businesses.
- National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB): The NFIB provides resources and advocacy for small businesses, including information on health insurance options, eligibility for tax credits, and assistance with navigating the ACA marketplace. The NFIB also offers workshops and webinars on health insurance for small businesses.
Health Insurance for Individuals and Families
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel overwhelming, especially when it comes to choosing the right plan for yourself and your family. Individual health insurance plans offer flexibility and customization, but understanding their costs and features is crucial for making informed decisions.
Cost Variations for Different Family Sizes and Income Levels
The cost of individual health insurance plans can vary significantly based on family size and income level. Premiums generally increase with the number of dependents covered. Additionally, individuals with higher incomes may face higher premiums, reflecting a greater ability to contribute to the cost of coverage.
- Family Size: A family of four will typically pay a higher premium than a single individual, as more people are covered under the plan.
- Income Level: Individuals with higher incomes may be subject to higher premiums, reflecting a greater ability to contribute to the cost of coverage.
- Age: Older individuals typically face higher premiums due to increased healthcare needs.
- Location: The cost of health insurance can vary by geographic location, reflecting differences in healthcare costs and provider networks.
Importance of Individual Health Needs and Coverage Requirements
When choosing an individual health insurance plan, it is crucial to consider individual health needs and coverage requirements. This involves evaluating factors such as pre-existing conditions, anticipated healthcare needs, and desired coverage levels.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing conditions may require specific coverage to address their ongoing healthcare needs. It is important to choose a plan that covers these conditions and provides access to necessary treatments.
- Anticipated Healthcare Needs: Consider anticipated healthcare needs, such as regular doctor visits, prescription medications, or potential future medical procedures. Select a plan that aligns with these needs and provides adequate coverage.
- Coverage Levels: Individual health insurance plans offer different levels of coverage, ranging from basic plans with limited benefits to comprehensive plans with extensive coverage. Choose a plan that meets your desired level of coverage and financial capabilities.
Managing Healthcare Costs and Maximizing Health Insurance Benefits
Managing healthcare costs effectively is a key aspect of individual health insurance. There are several strategies to minimize out-of-pocket expenses and maximize the benefits of your plan.
- Preventive Care: Take advantage of preventive care services covered by your plan, such as annual checkups and screenings. These services can help identify potential health issues early, reducing the need for more expensive treatments later.
- Generic Medications: When prescribed medications, consider generic options, which are typically more affordable than brand-name drugs. Discuss potential generic alternatives with your doctor.
- Negotiating Prices: For elective procedures or non-emergency medical services, inquire about pricing options and explore potential cost-saving strategies, such as negotiating with providers or considering alternative treatment centers.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): If eligible, consider using a Health Savings Account (HSA). HSAs allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars to pay for healthcare expenses, providing potential tax benefits and reducing out-of-pocket costs.
- Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs): Similar to HSAs, Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars to pay for healthcare expenses. FSAs can help manage healthcare costs by reducing taxable income.
Emerging Trends in Health Insurance Costs
Health insurance costs are a significant concern for individuals and families across the United States. While various factors contribute to these costs, certain emerging trends are shaping the future of health insurance premiums. These trends are fueled by advancements in healthcare technology, changing consumer preferences, and the ongoing struggle to manage rising healthcare expenditures.
Rising Prescription Drug Prices
Prescription drug costs have been a major driver of rising healthcare expenses. The increasing complexity of medications, coupled with limited competition in the pharmaceutical industry, has resulted in substantial price increases for many essential drugs. The impact of these rising prices is felt most acutely by individuals with chronic illnesses, who often rely on expensive medications to manage their conditions.
- One prominent example is the cost of insulin, a vital medication for individuals with diabetes. The price of insulin has risen dramatically in recent years, putting a significant financial burden on many patients.
- Another area of concern is the rising cost of specialty drugs, which are often used to treat complex or rare diseases. These drugs can be extremely expensive, with some costing tens of thousands of dollars per month.
The increasing cost of prescription drugs is likely to continue to impact health insurance premiums. As drug prices rise, insurers will need to adjust their premiums to cover the increased costs, ultimately passing these costs onto consumers.
Outcome Summary
Ultimately, understanding how much health insurance costs requires a nuanced approach that considers your individual circumstances, health needs, and financial goals. By leveraging the resources and information available, you can navigate the complexities of health insurance, secure affordable coverage, and gain peace of mind knowing you’re protected in the event of unexpected medical expenses.